Contents
I. Introduction

Welcome to the ultimate guide to sustainable eating and environmentally friendly foods. In today’s world, where climate change and environmental degradation are major concerns, it is crucial that we make conscious choices about the food we consume. Sustainable eating is not just about personal health, but also about the health of the planet.
So, what exactly is sustainable eating? It refers to a way of eating that minimizes the negative impact on the environment, supports local communities, and promotes the well-being of animals. It involves making informed choices about the food we buy, consume, and waste.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various aspects of sustainable eating, from understanding the environmental impact of different food choices to practical tips on how to incorporate sustainable practices into your daily life. Whether you are a seasoned environmentalist or just starting your journey towards sustainable living, this guide will provide you with valuable insights and actionable steps.
We will delve into topics such as organic farming, seasonal eating, reducing food waste, supporting local farmers, and the benefits of plant-based diets. We will also address common misconceptions and provide evidence-based information to help you make informed decisions.
By the end of this guide, you will have a deeper understanding of sustainable eating and be equipped with the knowledge and tools to make a positive impact on the environment through your food choices. So, let’s embark on this journey together and discover the power of sustainable eating!
II. Understanding Environmental Impact of Food

In today’s world, where sustainability and environmental consciousness are becoming increasingly important, it is essential to understand the environmental impact of the food we consume. From the carbon footprint of food production to water usage, deforestation, and food waste, every aspect of our food choices has consequences for the planet. In this section, we will delve into these issues and explore how our food choices can contribute to a more environmentally friendly future.
A. Carbon footprint of food production
One of the key factors contributing to the environmental impact of food is its carbon footprint. The carbon footprint refers to the amount of greenhouse gas emissions produced throughout the entire lifecycle of a product, including production, transportation, and disposal. When it comes to food production, several factors contribute to its carbon footprint.
Firstly, the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides in conventional agriculture releases significant amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These chemicals are often derived from fossil fuels, contributing to carbon emissions. Additionally, the intensive use of machinery, such as tractors and irrigation systems, also contributes to carbon emissions.
Furthermore, transportation plays a crucial role in the carbon footprint of food. The longer the distance food travels from farm to plate, the higher its carbon footprint. Therefore, opting for locally sourced and seasonal produce can significantly reduce the carbon emissions associated with food transportation.
Lastly, food waste is a major contributor to carbon emissions. When food is wasted, all the resources used in its production, including water, energy, and land, go to waste as well. Moreover, when food decomposes in landfills, it releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas. By reducing food waste and implementing efficient waste management systems, we can reduce the carbon footprint of our food.
B. Water usage in food production
Water is a precious resource, and its usage in food production is a significant environmental concern. Agriculture accounts for a substantial portion of global water consumption, and the inefficient use of water in farming practices can lead to water scarcity and environmental degradation.
Traditional irrigation methods, such as flood irrigation, can result in excessive water usage and water wastage. However, innovative irrigation techniques, such as drip irrigation and precision agriculture, can significantly reduce water consumption by delivering water directly to the plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff.
Moreover, certain crops require more water than others. For example, water-intensive crops like rice and almonds have a higher water footprint compared to vegetables and legumes. By choosing crops with lower water requirements and supporting sustainable farming practices, we can reduce the water footprint of our food.
C. Deforestation and agriculture
Deforestation is a critical environmental issue, and agriculture is a major driver of deforestation worldwide. Large-scale agricultural practices, such as the expansion of crop plantations and livestock grazing, often involve clearing forests to make way for agricultural land.
Deforestation not only leads to the loss of biodiversity and habitat destruction but also contributes to climate change. Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. When forests are cleared, the carbon stored in trees is released into the atmosphere, exacerbating greenhouse gas emissions.
To combat deforestation, it is crucial to support sustainable agricultural practices that prioritize forest conservation. This can be achieved through initiatives such as agroforestry, which involves integrating trees into agricultural landscapes, and promoting sustainable land management practices that preserve forests and biodiversity.
D. Food waste and its environmental consequences
Food waste is a significant environmental issue that has far-reaching consequences. Every year, a staggering amount of food is wasted globally, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions, water waste, and land degradation.
When food is wasted, all the resources used in its production, such as water, energy, and land, are wasted as well. Additionally, food waste that ends up in landfills decomposes and produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change.
To address the issue of food waste, various strategies can be implemented. These include improving supply chain management to reduce losses during transportation and storage, educating consumers about proper food storage and meal planning, and supporting initiatives that redirect surplus food to those in need.
By understanding the environmental impact of food production, we can make informed choices that contribute to a more sustainable future. From reducing our carbon footprint and water usage to supporting forest conservation and combating food waste, every action we take can make a difference. Together, we can create a more environmentally friendly food system that nourishes both people and the planet.
III. Sustainable Food Choices

In today’s world, making sustainable food choices is more important than ever. As a passionate advocate for the environment and a firm believer in the power of individual actions, I have dedicated myself to exploring and promoting sustainable eating habits. In this section, I will discuss various sustainable food choices that can have a positive impact on the environment.
A. Organic farming and its benefits
One of the most popular sustainable food choices is opting for organic farming. Organic farming practices prioritize the use of natural fertilizers and pesticides, avoiding harmful chemicals that can harm the environment and human health. By choosing organic produce, consumers support farmers who prioritize soil health, biodiversity, and water conservation.
Organic farming has numerous benefits for the environment. It helps reduce soil erosion, promotes healthy soil microbial activity, and preserves water quality by minimizing the use of synthetic fertilizers. Additionally, organic farming methods contribute to the overall health of ecosystems by supporting pollinators and other beneficial insects.
When consumers choose organic products, they are not only making a sustainable choice but also supporting a system that prioritizes the well-being of both people and the planet.
B. Locally sourced food and reducing food miles
Another important sustainable food choice is opting for locally sourced food. Choosing locally grown produce and locally raised meat reduces the carbon footprint associated with transportation and storage. By supporting local farmers and producers, consumers contribute to the local economy and help maintain agricultural diversity.
Reducing food miles, the distance food travels from farm to plate, is crucial in minimizing greenhouse gas emissions. When food is transported over long distances, it requires significant amounts of energy and contributes to air pollution. By choosing locally sourced food, consumers can significantly reduce their environmental impact and support sustainable agricultural practices.
C. Seasonal eating and its environmental advantages
Seasonal eating is not only a delicious way to enjoy fresh and flavorful food, but it also has numerous environmental advantages. When we consume fruits and vegetables that are in season, we reduce the need for energy-intensive storage and transportation methods.
Seasonal eating also supports local farmers by creating demand for their products during specific times of the year. By aligning our diets with the natural growing seasons, we can reduce the reliance on artificial growing methods and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
Furthermore, seasonal eating encourages biodiversity and helps preserve traditional crop varieties. By embracing the diversity of seasonal produce, we can support the resilience of ecosystems and contribute to a more sustainable food system.
D. Plant-based diets and their impact on sustainability
One of the most impactful sustainable food choices an individual can make is adopting a plant-based diet. Plant-based diets, which prioritize fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and nuts, have been proven to have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to diets rich in animal products.
Animal agriculture is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution. By reducing or eliminating the consumption of animal products, individuals can help mitigate climate change, conserve natural resources, and protect biodiversity.
Plant-based diets also offer numerous health benefits, including reduced risk of chronic diseases and improved overall well-being. By choosing plant-based options, individuals can make a positive impact on both their health and the environment.
IV. Sustainable Seafood

In today’s world, where environmental issues are at the forefront of our concerns, it is crucial to make sustainable choices in every aspect of our lives, including our food consumption. One area where we can make a significant impact is by choosing sustainable seafood. Sustainable seafood refers to fish and shellfish that are caught or farmed in a way that minimizes harm to the environment and ensures the long-term viability of the species and their habitats.
A. Importance of sustainable seafood
The importance of sustainable seafood cannot be overstated. Overfishing and destructive fishing practices have led to the depletion of fish stocks and the destruction of marine ecosystems. By opting for sustainable seafood, we can help protect marine biodiversity and ensure the health and resilience of our oceans for future generations.
Choosing sustainable seafood also has positive impacts on human health. Many unsustainable fishing practices involve the use of harmful chemicals and antibiotics, which can end up in the seafood we consume. By selecting sustainably sourced seafood, we can reduce our exposure to these harmful substances and enjoy a healthier diet.
B. Sustainable fishing practices
There are several sustainable fishing practices that help minimize the impact on marine ecosystems. One such practice is selective fishing, which involves targeting specific species and avoiding the capture of non-target species. This reduces bycatch, which is the unintentional capture of marine life, including endangered species.
Another sustainable fishing practice is the use of fishing gear that minimizes habitat damage. For example, using traps or pots instead of bottom trawling helps protect fragile habitats like coral reefs and seafloor ecosystems.
Additionally, implementing fishing quotas and size limits can help ensure that fish populations have the opportunity to reproduce and replenish their numbers. These measures, along with effective monitoring and enforcement, are essential for the long-term sustainability of our fisheries.
C. Seafood certification programs
Seafood certification programs play a crucial role in promoting sustainable fishing practices and helping consumers make informed choices. These programs assess and certify fisheries and aquaculture operations based on their environmental impact, adherence to sustainable practices, and traceability of their products.
One well-known certification program is the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC), which certifies wild-caught seafood. The MSC label ensures that the seafood comes from a fishery that meets strict sustainability standards, including the use of sustainable fishing methods and effective management practices.
Another reputable certification program is the Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC), which certifies responsibly farmed seafood. The ASC label guarantees that the seafood has been produced with minimal impact on the environment and in compliance with social responsibility standards.
D. Popular sustainable seafood options
When it comes to sustainable seafood options, there is a wide variety to choose from. Here are some popular choices:
- Alaskan salmon: Alaskan salmon is known for its sustainable fishing practices and well-managed fisheries. It is a delicious and nutritious choice that is also rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
- Atlantic mackerel: Atlantic mackerel is a fast-growing species that is abundant in the Atlantic Ocean. It is a sustainable choice that is high in omega-3 fatty acids and low in contaminants.
- Pacific sardines: Pacific sardines are small, oily fish that are a sustainable and affordable seafood option. They are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and are a versatile ingredient in various dishes.
- US farmed oysters: Oysters are filter feeders that help improve water quality and promote a healthy marine ecosystem. US farmed oysters are a sustainable choice that is also delicious and packed with nutrients.
- Arctic char: Arctic char is a cold-water fish that is sustainably farmed in recirculating aquaculture systems. It is a flavorful and nutritious alternative to salmon.
By choosing these sustainable seafood options, we can enjoy delicious meals while also contributing to the preservation of our oceans and the well-being of future generations.
V. Sustainable Meat and Dairy
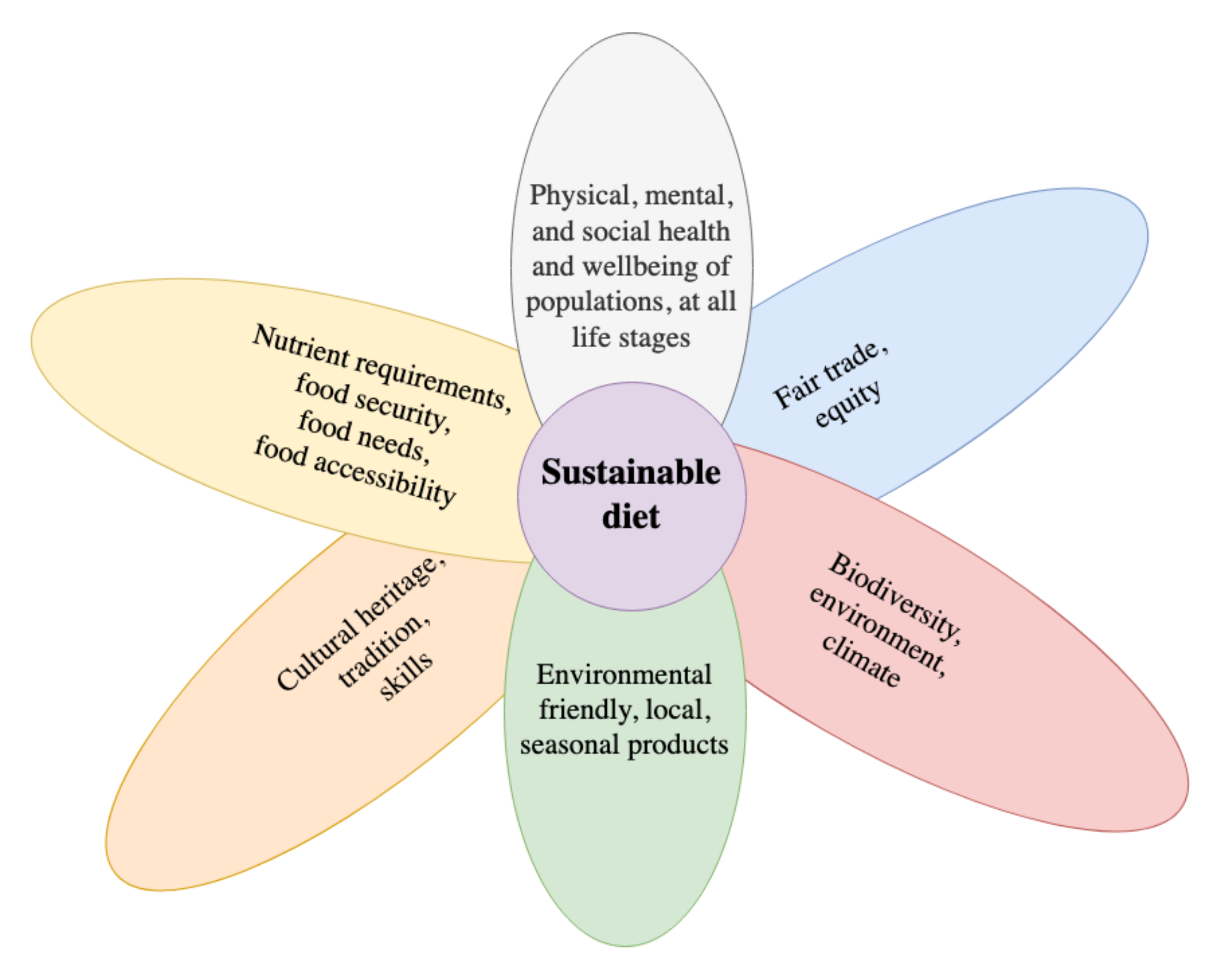
In today’s world, where environmental concerns are at the forefront of many discussions, it is essential to consider the impact of our food choices on the planet. The production of meat and dairy products, in particular, has been linked to significant environmental issues. In this section, we will explore the environmental impact of meat and dairy production, discuss ways to reduce meat consumption for sustainability, explore grass-fed and organic meat options, and highlight sustainable dairy alternatives.
A. Environmental Impact of Meat and Dairy Production
The production of meat and dairy products has a significant impact on the environment. One of the main concerns is greenhouse gas emissions. Livestock farming, including the cultivation of animal feed and the processing of meat and dairy products, is responsible for a substantial amount of global greenhouse gas emissions. According to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization, the livestock sector is responsible for approximately 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions, which is more than the emissions from the entire transportation sector.
In addition to greenhouse gas emissions, meat and dairy production also contribute to deforestation. Large areas of forests are cleared to make way for livestock farming and the cultivation of animal feed crops. Deforestation not only leads to the loss of biodiversity but also contributes to climate change as trees play a crucial role in absorbing carbon dioxide.
Furthermore, the intensive use of water and land resources in meat and dairy production is a cause for concern. Livestock farming requires vast amounts of water for animal hydration, feed production, and processing. Additionally, large areas of land are needed for grazing and growing animal feed crops, leading to habitat destruction and soil degradation.
It is clear that the production of meat and dairy products has a significant environmental impact. As consumers, we have the power to make more sustainable choices to mitigate these effects.
B. Reducing Meat Consumption for Sustainability
One of the most effective ways to reduce the environmental impact of meat and dairy production is to decrease our meat consumption. By adopting a more plant-based diet, we can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and land degradation associated with livestock farming.
There are several approaches to reducing meat consumption. One option is to become a flexitarian, which involves primarily consuming plant-based foods while occasionally including meat and dairy products in the diet. This approach allows for flexibility while still promoting sustainability.
Another approach is to embrace meatless meals. Incorporating more vegetarian and vegan recipes into our weekly meal plans can have a positive impact on the environment. Plant-based proteins, such as legumes, tofu, and tempeh, can provide the necessary nutrients while reducing the reliance on animal products.
Additionally, choosing to support local and sustainable meat producers can make a difference. By purchasing meat from farmers who prioritize animal welfare and employ sustainable farming practices, we can contribute to a more environmentally friendly food system.
C. Grass-fed and Organic Meat Options
For those who choose to continue consuming meat, opting for grass-fed and organic options can be a more sustainable choice. Grass-fed meat comes from animals that have been raised on a natural diet of grass and pasture, rather than being fed with grain-based feed. This method of farming promotes healthier animals, reduces the need for intensive feed production, and helps sequester carbon in the soil.
Organic meat, on the other hand, is produced without the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, antibiotics, or hormones. Organic farming practices prioritize animal welfare, biodiversity, and soil health. By choosing organic meat, consumers can support a more sustainable and ethical approach to meat production.
D. Sustainable Dairy Alternatives
For those looking to reduce their dairy consumption or eliminate it altogether, there are a variety of sustainable dairy alternatives available. Plant-based milk alternatives, such as almond milk, soy milk, oat milk, and coconut milk, offer a more environmentally friendly option. These alternatives require fewer resources, produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions, and have a lower impact on land and water resources compared to traditional dairy production.
Furthermore, plant-based dairy alternatives can provide similar nutritional benefits as dairy milk. Many of these alternatives are fortified with essential vitamins and minerals, making them a suitable choice for individuals with dietary restrictions or preferences.
VI. Sustainable Agriculture Practices
A. Regenerative agriculture and its benefits
Regenerative agriculture is a farming practice that focuses on improving and revitalizing the health of the soil, rather than depleting it. This approach goes beyond sustainable agriculture by actively working to restore and regenerate the soil ecosystem. As an advocate for sustainable eating, I have personally witnessed the transformative effects of regenerative agriculture on both the environment and food quality.
One of the key benefits of regenerative agriculture is its ability to sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in the soil. This process, known as carbon sequestration, helps mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, regenerative farming practices promote biodiversity, enhance water retention, and improve soil fertility.
By implementing regenerative agriculture techniques such as cover cropping, crop rotation, and minimal tillage, farmers can restore soil health and reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. This not only benefits the environment but also leads to healthier and more nutritious food for consumers.
B. Permaculture and sustainable farming techniques
Permaculture is a holistic approach to sustainable farming that aims to create self-sustaining ecosystems that mimic natural patterns and processes. It involves designing agricultural systems that are resilient, diverse, and productive, while minimizing the use of external inputs.
Permaculture principles include observing and working with nature, using renewable resources, and maximizing energy efficiency. By utilizing techniques such as companion planting, agroforestry, and water harvesting, permaculture farmers can create highly productive and sustainable food systems.
As someone who has practiced permaculture on my own small-scale farm, I have experienced firsthand the benefits of this approach. Not only does permaculture promote environmental sustainability, but it also fosters a sense of connection and harmony with the natural world.
C. Agroforestry and its role in sustainable agriculture
Agroforestry is a land management system that combines trees or shrubs with crops or livestock. This practice offers numerous benefits for sustainable agriculture, including improved soil health, increased biodiversity, and enhanced climate resilience.
By integrating trees into agricultural landscapes, agroforestry systems provide shade, windbreaks, and habitat for beneficial insects and wildlife. They also help prevent soil erosion, regulate water cycles, and sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
As an advocate for sustainable eating, I strongly believe in the importance of incorporating agroforestry practices into our agricultural systems. By diversifying our farms with trees and integrating them into our food production, we can create more resilient and sustainable food systems for future generations.
D. Crop rotation and soil health
Crop rotation is a fundamental practice in sustainable agriculture that involves growing different crops in a specific sequence on the same piece of land. This technique helps maintain soil fertility, control pests and diseases, and reduce the need for synthetic inputs.
By rotating crops, farmers can break pest and disease cycles, as different crops have different nutrient requirements and vulnerabilities. This reduces the reliance on chemical pesticides and fertilizers, leading to healthier soils and ecosystems.
Furthermore, crop rotation can improve soil structure and nutrient availability. Certain crops, such as legumes, have the ability to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere and make it available to other plants. This reduces the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers and promotes a more sustainable and balanced nutrient cycle.
As a sustainable agriculture advocate, I encourage farmers to adopt crop rotation practices to enhance soil health and reduce environmental impact. By implementing diverse crop rotations, we can create resilient and productive agricultural systems that benefit both the environment and our food supply.
VII. Food Packaging and Waste Reduction
Food packaging plays a significant role in our daily lives, ensuring the safety and preservation of our food. However, it also has a substantial impact on the environment. As an environmentally conscious individual, I believe it is crucial to understand the environmental implications of food packaging and explore sustainable alternatives. In this section, we will delve into the impact of food packaging on the environment, sustainable packaging alternatives, recycling and waste management in the food industry, and tips for reducing food waste at home.
A. Impact of food packaging on the environment
Food packaging has a considerable environmental footprint, contributing to pollution, resource depletion, and greenhouse gas emissions. The production and disposal of packaging materials, such as plastic, contribute to the accumulation of waste in landfills and oceans. Plastic packaging, in particular, poses a severe threat to marine life and ecosystems.
Furthermore, the manufacturing of packaging materials requires significant amounts of energy and natural resources, further exacerbating environmental degradation. The extraction of raw materials, such as petroleum for plastic production, contributes to habitat destruction and air pollution.
To mitigate the environmental impact of food packaging, it is essential to explore sustainable alternatives that minimize waste and promote resource conservation.
B. Sustainable packaging alternatives
Fortunately, there are various sustainable packaging alternatives available that can help reduce the environmental impact of food packaging. These alternatives include:
- Biodegradable packaging: Biodegradable materials, such as plant-based plastics and compostable packaging, break down naturally over time, reducing the accumulation of waste in landfills.
- Recyclable packaging: Packaging materials that can be easily recycled, such as glass, aluminum, and certain types of plastics, help conserve resources and reduce waste.
- Reusable packaging: Encouraging the use of reusable containers and packaging, such as glass jars and stainless steel lunch boxes, can significantly reduce single-use packaging waste.
- Minimalist packaging: Adopting minimalist packaging designs that use fewer materials and prioritize recyclability can help minimize waste and reduce the environmental impact.
By choosing sustainable packaging alternatives, we can contribute to a more environmentally friendly food system.
C. Recycling and waste management in the food industry
The food industry plays a crucial role in implementing effective recycling and waste management practices. By adopting sustainable waste management strategies, the industry can significantly reduce its environmental footprint. Some key initiatives include:
- Implementing comprehensive recycling programs: Food businesses can establish recycling programs that encourage employees and customers to recycle packaging materials properly.
- Partnering with recycling facilities: Collaborating with local recycling facilities ensures that packaging materials are properly processed and recycled.
- Reducing packaging waste: The food industry can work towards minimizing packaging waste by adopting sustainable packaging practices, such as using recyclable or biodegradable materials.
- Supporting composting initiatives: Encouraging the composting of food waste and packaging materials can divert organic waste from landfills and promote nutrient-rich soil.
By prioritizing recycling and waste management, the food industry can contribute to a more sustainable and circular economy.
D. Tips for reducing food waste at home
Food waste is a significant issue that contributes to environmental degradation and resource depletion. By adopting simple practices at home, we can reduce food waste and minimize our environmental impact. Here are some tips:
- Plan meals and create shopping lists: Planning meals in advance and creating shopping lists help prevent over-purchasing and reduce the likelihood of food waste.
- Proper storage: Storing food correctly, such as using airtight containers and refrigerating perishable items, helps prolong their freshness and reduces the chances of spoilage.
- First in, first out: When organizing your pantry and refrigerator, practice the “first in, first out” principle, ensuring that older items are used before newer ones.
- Portion control: Serve appropriate portion sizes to avoid leftovers that may go to waste.
- Get creative with leftovers: Instead of discarding leftovers, find creative ways to repurpose them into new meals or freeze them for future use.
- Composting: If you have access to composting facilities, consider composting food scraps to divert organic waste from landfills and create nutrient-rich soil.
By implementing these tips, we can significantly reduce food waste and contribute to a more sustainable food system.
VIII. Sustainable Eating on a Budget
In today’s world, where environmental concerns are at the forefront of many people’s minds, sustainable eating has become increasingly popular. However, one common misconception is that eating sustainably is expensive. In reality, there are plenty of affordable options for those on a budget who still want to make environmentally friendly food choices. In this section, we will explore some affordable sustainable food options, meal planning and reducing food waste, growing your own food, and community-supported agriculture programs.
A. Affordable sustainable food options
When it comes to sustainable eating on a budget, it’s important to focus on whole foods that are locally sourced and in season. These foods tend to be more affordable and have a lower environmental impact compared to processed or imported foods. Here are some affordable sustainable food options:
- Beans and legumes: These are not only affordable but also high in protein and fiber. They can be used in a variety of dishes such as soups, stews, and salads.
- Seasonal fruits and vegetables: Buying fruits and vegetables that are in season not only supports local farmers but also ensures that you are getting the freshest produce at a lower cost.
- Whole grains: Foods like brown rice, quinoa, and oats are not only nutritious but also budget-friendly. They can be used as a base for many meals.
- Plant-based proteins: Opting for plant-based proteins like tofu, tempeh, and seitan can be more affordable than animal-based proteins. They are also more sustainable as they require fewer resources to produce.
- Locally sourced meat and seafood: If you do consume animal products, choosing locally sourced and sustainably raised meat and seafood can be more affordable than buying from large-scale industrial farms.
By incorporating these affordable sustainable food options into your diet, you can make a positive impact on the environment without breaking the bank.
B. Meal planning and reducing food waste
Meal planning is a great way to save money and reduce food waste. By planning your meals in advance, you can make sure that you only buy the ingredients you need and avoid impulse purchases. Here are some tips for meal planning and reducing food waste:
- Create a weekly meal plan: Take some time each week to plan out your meals and make a shopping list. This will help you avoid buying unnecessary items and ensure that you have everything you need for your meals.
- Buy in bulk: Buying staple items like grains, beans, and spices in bulk can save you money in the long run. Just make sure to store them properly to maintain their freshness.
- Use leftovers creatively: Instead of throwing away leftovers, find creative ways to repurpose them into new meals. For example, leftover roasted vegetables can be turned into a delicious frittata or added to a salad.
- Compost food scraps: If you have food scraps that can’t be used, consider starting a compost bin. This will not only reduce waste but also create nutrient-rich soil for your garden.
By implementing these meal planning and food waste reduction strategies, you can save money and minimize your impact on the environment.
C. Growing your own food
One of the most sustainable and cost-effective ways to eat is by growing your own food. Whether you have a large backyard or a small balcony, there are plenty of options for growing your own fruits, vegetables, and herbs. Here are some benefits of growing your own food:
- Cost savings: Growing your own food can significantly reduce your grocery bill. Seeds and seedlings are relatively inexpensive, and the produce you grow is essentially free.
- Freshness and flavor: There’s nothing quite like the taste of freshly picked produce. When you grow your own food, you have control over how it’s grown and can enjoy the freshest, most flavorful fruits and vegetables.
- Environmental impact: By growing your own food, you can reduce the carbon footprint associated with transporting and packaging produce. You also have the opportunity to use organic and sustainable gardening practices.
- Connection to nature: Gardening is a great way to connect with nature and reduce stress. It can be a rewarding and therapeutic activity that provides a sense of accomplishment.
Even if you don’t have a green thumb, there are plenty of resources available to help you get started with gardening. From online tutorials to community gardening programs, you can find the support you need to grow your own food.
D. Community-supported agriculture programs
Community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs are another great way to eat sustainably on a budget. These programs allow you to purchase a share of a local farm’s harvest in advance, usually on a seasonal basis. Here are some benefits of participating in a CSA program:
- Fresh, local produce: By joining a CSA program, you have access to fresh, locally grown produce that is often harvested the same day or week it is delivered to you.
- Support for local farmers: CSA programs provide direct support to local farmers, helping them sustain their operations and continue growing food in a sustainable manner.
- Cost savings: While the upfront cost of a CSA share may seem high, it often works out to be more affordable than buying the same amount of produce at a grocery store. Plus, you get the added benefit of supporting local farmers.
- Connection to the community: Participating in a CSA program allows you to connect with other members of your community who share a passion for sustainable eating and supporting local agriculture.
CSA programs are a win-win for both consumers and farmers. They provide a reliable source of income for farmers and allow consumers to enjoy fresh, local produce at an affordable price.
IX. Sustainable Eating in Restaurants
When it comes to sustainable eating, making environmentally friendly choices extends beyond the kitchen. Dining out at restaurants can also have an impact on the planet. In this section, we will explore various aspects of sustainable eating in restaurants and how you can make conscious choices to support a greener foodservice industry.
A. Choosing sustainable restaurants
One of the first steps in sustainable eating is selecting restaurants that prioritize eco-friendly practices. Look for establishments that source their ingredients locally, support organic farming, and promote sustainable agriculture. These restaurants often have a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and supporting local communities.
Additionally, consider restaurants that have implemented waste reduction strategies. This can include composting food waste, using biodegradable or reusable packaging, and minimizing single-use plastics. By choosing these establishments, you are supporting their efforts to reduce waste and contribute to a more sustainable future.
B. Farm-to-table dining and its benefits
Farm-to-table dining has gained popularity in recent years, and for good reason. This concept involves restaurants sourcing their ingredients directly from local farms, ensuring freshness and reducing transportation emissions. By opting for farm-to-table dining, you can enjoy meals made with seasonal, locally sourced produce and support local farmers.
In addition to the environmental benefits, farm-to-table dining also offers health advantages. Locally sourced ingredients are often harvested at their peak ripeness, meaning they are packed with nutrients and flavor. These meals are not only better for the planet but also for your well-being.
C. Sustainable seafood options at restaurants
Seafood lovers can make sustainable choices when dining out by selecting restaurants that offer sustainable seafood options. Overfishing and destructive fishing practices have had a significant impact on marine ecosystems. By choosing seafood that is sustainably sourced, you can help protect vulnerable species and support responsible fishing practices.
Look for restaurants that follow guidelines set by organizations such as the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) or the Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC). These certifications ensure that the seafood served is caught or farmed in a way that minimizes environmental impact and promotes the long-term health of our oceans.
D. Encouraging sustainable practices in the foodservice industry
As consumers, we have the power to influence change in the foodservice industry. By actively supporting sustainable practices and voicing our preferences, we can encourage restaurants to adopt more eco-friendly measures. Here are some ways you can make a difference:
- Choose restaurants that prioritize sustainability and make it known that this is an important factor in your dining decisions.
- Engage with restaurant owners and managers, expressing your support for sustainable practices and encouraging them to implement changes.
- Spread the word about sustainable restaurants through word-of-mouth, social media, and online reviews.
- Support organizations and initiatives that promote sustainable eating in the foodservice industry.
By collectively taking these actions, we can create a demand for sustainable practices in the restaurant industry and contribute to a more environmentally friendly future.

William Black is a seasoned wordsmith with a passion for crafting compelling content. Hailing from the vibrant city of Seattle, he has honed his writing skills through years of experience in the field. William holds a Bachelor’s degree in English Literature from the prestigious University of Washington, where he developed a deep appreciation for the power of storytelling. His educational background has equipped him with a keen eye for detail and a strong command of the English language. With a particular expertise in SEO writing, William effortlessly weaves keywords into his prose, ensuring maximum visibility and engagement. When he’s not busy crafting captivating content, you can find William exploring the local food scene, indulging in his love for all things culinary.
